


Here's a 9-step guide to help you make your 529 savings go as far as possible.
List of 529 eligible expenses trial#
But learning by trial and error can be costly at tax time, and more importantly, your child could lose out on financial aid if you're not careful. What can you use this money for? Which expenses trigger taxes and penalties? If you do things right, no penalties or federal income tax-and, in many states, no state income tax-will be due on your withdrawals. However, with "accelerated gifting," * a 529 account can be funded with contributions of $85,000 per person or $170,000 per couple-which uses up your federal gift-tax exclusion for 5 years. Contributing more than $17,000 per beneficiary would need to be reported to the IRS as a gift. Grandparents can also contribute up to $34,000 per beneficiary per year. You’ll be in control of how much is withdrawn and how it'll be used, but there are a few things you need to know up front to make the most of your savings.įirst a reminder-you can save up to $17,000 per parent in a 529 account, or $34,000 per couple.

Now college is closer and it's time to think about spending the money you've put aside. Additional Informationįor additional information, refer to Publication 970, Tax Benefits for Education.Year after year, you and your child have been saving for college through a 529 savings account. Form 1099-Q should be made available to you by January 31, 2023. The amount of your gross distribution (box 1) shown on each form will be divided between your earnings (box 2) and your basis or return of investment (box 3). You should receive a Form 1099-Q, Payments from Qualified Education Programs (Under Sections 529 and 530) from each of the programs from which you received a QTP distribution. Interest paid with these funds doesn't qualify for the student loan interest deduction. The amount of distributions for loan repayments of any individual is limited to $10,000 lifetime. Amounts can be withdrawn to pay principal or interest on a designated beneficiary's or their sibling's student loan.However, if the amount of a distribution is greater than the beneficiary's qualified higher education expenses (including tuition at an elementary or secondary public, private, or religious school), a portion of the earnings is taxable. Distributions aren't taxable when used to pay for qualified higher education expenses (including tuition at an elementary or secondary public, private, or religious school).The beneficiary doesn't generally have to include the earnings from a QTP as income.
List of 529 eligible expenses free#
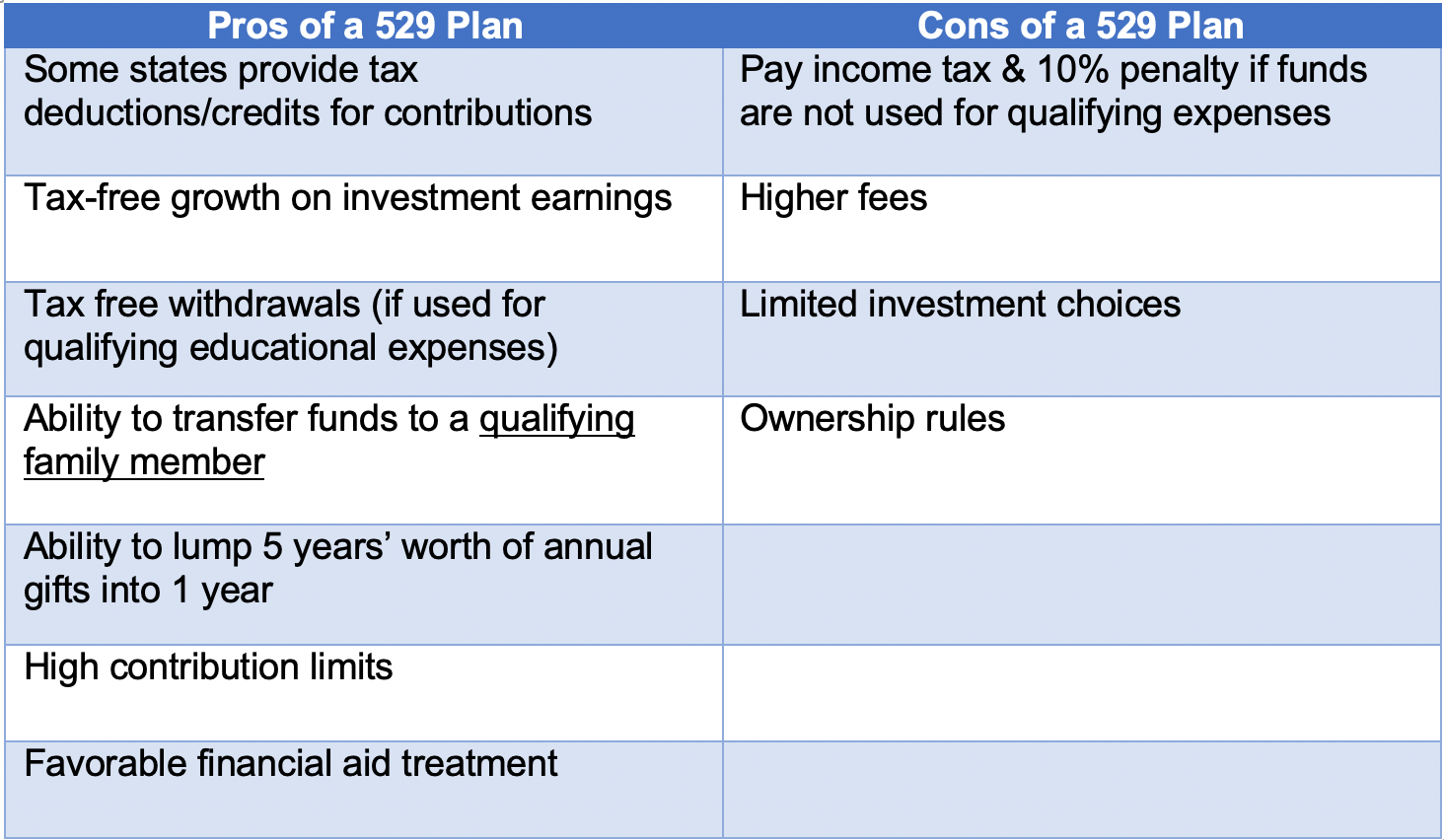
Qualified higher education expenses generally include expenses required for the enrollment or attendance of the designated beneficiary at any college, university, vocational school, or other postsecondary educational institution eligible to participate in a student aid program administered by the Department of Education. Eligible educational institutions can also establish and maintain QTPs but only to allow prepaying a beneficiary's qualified higher education expenses. A qualified tuition program (QTP), also referred to as a section 529 plan, is a program established and maintained by a state, or an agency or instrumentality of a state, that allows a contributor either to prepay a beneficiary's qualified higher education expenses at an eligible educational institution or to contribute to an account for paying those expenses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
